Plastic Compounds Outperform Ceramics in Automotive Navigation Antennas

Sabic has debuted two LNP Thermocomp compounds that offer the potential to improve signal gain performance compared with ceramics in second-generation automotive global navigation satellite system (GNSS) antennas. The LNP Thermocomp ZKC0CXXD and ZKC0DXXD compounds help enable the design and molding of antenna substrates with more-complex pattern markings that add effective surface area, a critical factor in enhancing signal capture.
For customers that currently use ceramics, switching to the LNP Thermocomp compounds can help lower system costs by avoiding secondary operations while improving antenna performance. Designers and engineers who find incumbent materials inadequate for developing novel, high-resolution GNSS antennas can help address new requirements with the Sabic products.
Improved signal capture and design freedom
“As GNSS antenna technology advances to its second generation with higher resolution, Sabic continues to enhance the scope and capabilities of our LNP specialty compounds portfolio to meet new performance requirements,” said Joshua Chiaw, director of business management, LNP & Noryl. “Our new LNP Thermocomp compounds can help antenna manufacturers achieve superior signal gain compared to ceramic substrates. They also provide flexibility to produce smaller parts with the same performance as ceramic, or equal-size parts with better performance. This remarkable combination of improved signal capture and design freedom, plus system cost advantages, can help propel innovation in GNSS technology — a keystone of occupant safety today and autonomous driving in the future.”
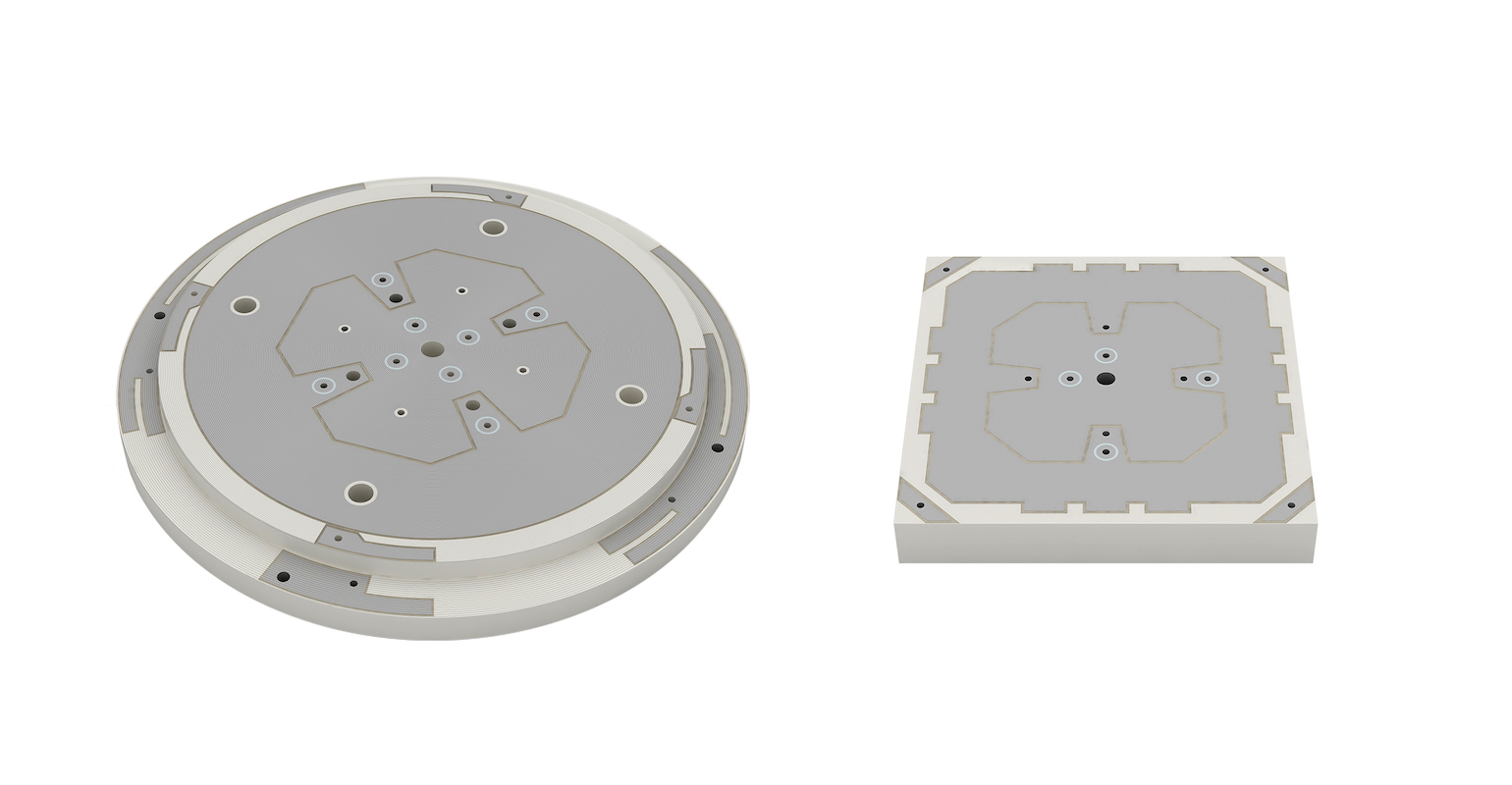
The LNP Thermocomp compounds, which offer a high dielectric constant (Dk) for miniaturization and a low dissipation factor (Df) to facilitate signal acquisition, can be tailored to meet the electrical requirements of individual applications. They feature electroplating capability, good thermal resistance for reliability, and the design freedom and production efficiency of thermoplastics. Both are well-suited for shark-fin-style and new conformal antenna designs.
Plastic compounds enable intricate patterns
The antenna serves as the front end of the GNSS signal processing chain. Optimal signal gain requires maximum surface area to capture radio signals from satellites. Second-generation GNSS antennas operate by combining signals from satellites with two different frequencies for high resolution, making signal capture even more demanding. To expand the effective surface area of the antenna substrate, manufacturers create complex pattern markings. However, ceramic materials are restricted in the shape and complexity of patterns that can be used because of challenges in applying metal plating to small or constrained spaces. These factors can affect antenna performance and limit the suitability of ceramics for high-resolution GNSS systems.
By contrast, Sabic’s new LNP Thermocomp compounds can be easily injection molded into antenna substrates with a wide range of pattern markings. Intricate shapes, indentations, and other elements can significantly increase an existing part’s effective surface area, supporting the stringent signal gain requirements of high-resolution GNSS antennas. Unlike plated ceramics, these compounds deliver a high yield rate following copper-, nickel-, and silver-plating processes, thanks to their stable electroplating capability.
The new Sabic materials also help to reduce system costs compared to ceramic substrates, which require time-consuming secondary operations such as shaping, drilling, and polishing. Injection molding with LNP Thermocomp compounds can deliver higher throughput and productivity and reduce scrap to keep costs down.
“Our renowned innovation capabilities position Sabic to respond quickly to technical trends, such as the increasingly high resolution of GNSS antennas,” said Jenny Wang, Director, Formulation and Application, APAC. “We support our plastic compounds with a broad array of application development resources. For instance, we can simulate antenna performance using the wide range of dielectric properties of our compounds to fine-tune thermoplastic substrate materials that are well-suited for specific antenna designs. Our Global Application Technology centers offer sophisticated engineering, testing, analysis, and customization services to help ensure customer success.”

Leave a Reply